KR-IST - Lecture 4b Heuristic search in Java
Chris Thornton
Introduction
This lecture (which may be skipped if we are behind time) works
through an implementation of heurstic search for the 8-puzzle.
Node class
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int[] state = new int[9];
int cost;
Node parent = null;
Vector<Node> successors = new Vector<Node>();
Node(int s[], Node parent) {
this.parent = parent;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) state[i] = s[i];
}
public String toString() {
String s = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
s = s + state[i] + " "; }
return s;
}
Node class cont.
public boolean equals(Node n) {
boolean result = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
if (n.state[i] != state[i]) result = false; }
return result;
}
Vector<Node> getPath(Vector<Node> v) {
v.insertElementAt(this, 0);
if (parent != null) v = parent.getPath(v);
return v;
}
Vector<Node> getPath() {
return getPath(new Vector<Node>()); }
}
Space representation
class EightPuzzleSpace {
Node getRoot() {
int ex[] = {3, 1, 2, 4, 7, 5, 6, 8, 0};
int rn[] = {7, 2, 4, 5, 0, 6, 8, 3, 1}; // the Russell and Norvig eg
return new Node(ex, null);
}
Node getGoal() {
int state[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};
return new Node(state, null);
}
Node transformState(int r0, int c0, int r1, int c1, Node parent) {
int[] s = parent.state;
int[] newState = {s[0], s[1], s[2], s[3], s[4], s[5], s[6], s[7], s[8]};
newState[(r1 * 3) + c1] = s[(r0 * 3) + c0];
newState[(r0 * 3) + c0] = 0;
return new Node(newState, parent);
}
Successsor function
Vector<Node> getSuccessors(Node parent) {
Vector<Node> successors = new Vector<Node>();
for (int r = 0; r < 3; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++) {
if (parent.state[(r * 3) + c] == 0) { /* hole here */
if (r > 0) { /* move tile from left */
successors.add(transformState(r-1, c, r, c, parent)); }
if (r < 2) { /* move tile from right */
successors.add(transformState(r+1, c, r, c, parent)); }
if (c > 0) { /* move tile from below */
successors.add(transformState(r, c-1, r, c, parent)); }
if (c < 2) { /* move tile from above */
successors.add(transformState(r, c+1, r, c, parent)); }
}
}
}
parent.successors = successors; /* used in getTree */
return successors;
}
}
Search representation
public class EightPuzzleSearch {
EightPuzzleSpace space = new EightPuzzleSpace();
Vector<Node> open = new Vector<Node>();
Vector<Node> closed = new Vector<Node>();
int h1Cost(Node node) {
int cost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < node.state.length; i++) {
if (node.state[i] != i) cost++; }
return cost;
}
The h2 heuristic
int h2Cost(Node node) {
int cost = 0;
int state[] = node.state;
for (int i = 0; i < state.length; i++) {
int v0 = i, v1 = state[i];
if (v1 == 0) continue; /* don't count the hole */
int row0 = v0 / 3, col0 = v0 % 3, row1 = v1 / 3, col1 = v1 % 3;
int c = (Math.abs(row0 - row1) + Math.abs(col0 - col1));
cost += c; }
return cost;
}
int hCost(Node node) { /* set to call either h1 or h2 */
return h2Cost(node);
}
Node selection
Node getBestNode(Vector nodes) {
int index = 0, minCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++) {
Node node = (Node)nodes.elementAt(i);
if (node.cost < minCost) {
minCost = node.cost;
index = i; } }
Node bestNode = (Node)nodes.remove(index);
return(bestNode);
}
Node getUniqueNode(Node node) {
int i = open.indexOf(node);
if (i != -1) {
node = open.get(i); }
else if ((i = closed.indexOf(node)) != -1) {
node = closed.get(i); }
return(node);
}
run method
void printPath(Vector path) {
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(" " + path.elementAt(i) + "\n"); }
}
void run() {
Node root = space.getRoot();
Node goal = space.getGoal();
Node solution = null;
open.add(root);
System.out.print("\nRoot: " + root + "\n\n");
Main loop
while (open.size() > 0) {
Node node = getBestNode(open);
int pathLength = node.getPath().size();
closed.add(node);
if (node.equals(goal)) { solution = node; break; }
Vector<Node> successors = space.getSuccessors(node);
for (int i = 0; i < successors.size(); i++) {
Node successor = getUniqueNode(successors.get(i));
int cost = hCost(successor) + pathLength + 1;
int previousCost = successor.cost;
boolean inClosed = closed.contains(successor);
boolean inOpen = open.contains(successor);
if (!(inClosed || inOpen)
|| cost < previousCost) {
if (inClosed) closed.remove(successor);
if (!inOpen) open.add(successor);
successor.cost = cost;
successor.parent = node;
}
}
}
Solution printing
// new TreePrint(getTree(root));
if (solution != null) {
Vector path = solution.getPath();
System.out.print("\nSolution found\n");
printPath(path); }
}
public static void main(String args[]) { // do the search
new EightPuzzleSearch().run();
}
}
Search space explored
Root: 3 1 2 4 7 5 6 8 0
3 1 2 4 7 5 6 8 0
|-- 3 1 2 4 7 0 6 8 5
|-- 3 1 2 4 7 5 6 0 8
|-- 3 1 2 4 0 5 6 7 8
| |-- 3 0 2 4 1 5 6 7 8
| |-- 3 1 2 4 7 5 6 0 8
| |-- 3 1 2 0 4 5 6 7 8
| | |-- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| | |-- 3 1 2 6 4 5 0 7 8
| | |-- 3 1 2 4 0 5 6 7 8
| |-- 3 1 2 4 5 0 6 7 8
|-- 3 1 2 4 7 5 0 6 8
|-- 3 1 2 4 7 5 6 8 0
Solution path
3 1 2 4 7 5 6 8 0
3 1 2 4 7 5 6 0 8
3 1 2 4 0 5 6 7 8
3 1 2 0 4 5 6 7 8
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
.
Summary
- Node class
- Space representation
- Successsor function
- Search representation
- Node selection
- Main loop
- main method
- Output
Questions
- What are the main shortcomings of the EightPuzzleSearch
program?
- This program uses a `linear' representation of the board
state. What method is used for translating between 2d cell
references and 1d array subscripts?
- The program uses an explicit map for associating nodes
with parents. Why is it necessary to represent this
information and what alternative strategies are there?
- Russell and Norvig focus on 8-puzzle goal states in which
the hole is in the top-right corner. What impact does use of
this form of goal have on the computation of the h1 function?
- Where and how is the g element of the heuristic value
calculated?
- What is the point of moving nodes back to OPEN once they
have already been placed on CLOSED?
Exercises
- Turn the program into a 5-puzzle solver, i.e., modify it so as to use
a board with three columns and two rows.
- Rewrite the successor function so as to use a 2d state
representation, i.e., an array where the the rows and columns of the
array correspond directly to the arrays and columns of the board state.
- Modify the h2 definition so that it uses the Euclidean distance
rather than the City-block distance as a basis for evaluation. The
Euclidean distance between two points
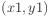 and
and 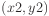 may be calculated as
may be calculated as
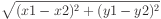
- Measure the different between the performance of this version of h2
and the original version.
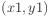 and
and 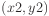 may be calculated as
may be calculated as 
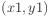 and
and 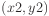 may be calculated as
may be calculated as